The integral of f(x)=x.
Given a natural number n>0, consider the following
dissection of the interval [0,2]: ![]() .
Consider next these two step functions:
.
Consider next these two step functions: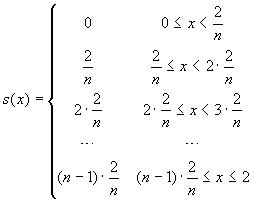 ,
,
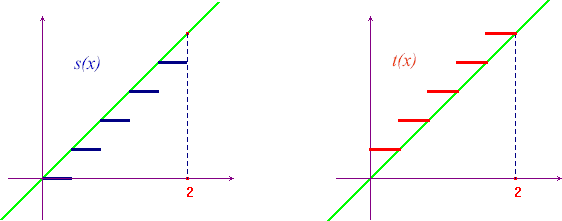
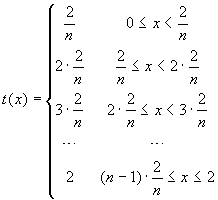 , whose graphs are represented here below,
in the case n = 5.
, whose graphs are represented here below,
in the case n = 5.
Let's now calculate the integrals of these two step
functions .![]() =
= ![]() ,
where we have used the formula for the sum of an arithmetic
progression. Using the same strategy we obtain
,
where we have used the formula for the sum of an arithmetic
progression. Using the same strategy we obtain 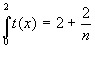
If n gets greater and greater these two step functions
become closer and closer to f(x)=x, and their integrals
tend to the common value 2. It's almost obvious that 2 is
the supremum of the integrals of all lower step approximations
of f, and, at the same time, the infimum of the
integrals of all upper step approximations of f. So
![]() . Observe that the area between the function
and the x-axis can also be calculated by elementary
techniques, with the same value.
. Observe that the area between the function
and the x-axis can also be calculated by elementary
techniques, with the same value.